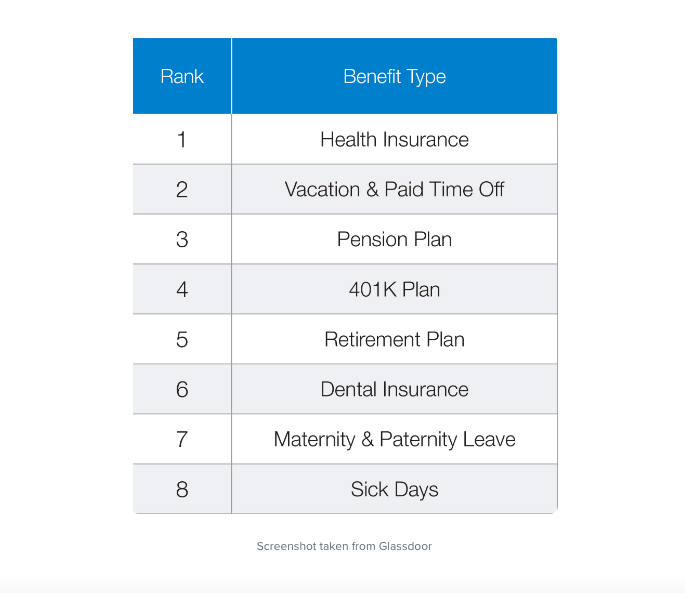
Benefit rankings
What are employee benefits?
Employee benefits are additional perks or resources that companies offer to their employees in addition to their salary or wages. These benefits can be financial or non-financial in nature, and they are designed to improve the overall employment experience and provide additional support and resources to employees.
Examples of financial employee benefits might include things like health insurance, a pension scheme, or a bonus pay structure. Non-financial employee benefits might include things like flexible working arrangements, training and development opportunities, or employee discounts.
Employee benefits can be an important factor in attracting and retaining top talent, and they can also help to improve employee satisfaction and engagement. Companies may offer a range of different employee benefits, depending on their size, industry, and location, and the specific benefits offered may vary from one company to another.
What are the top ten employee benefits in the UK?
There are many different benefits that companies may offer to their employees in the UK, and the specific benefits offered may vary depending on the size, industry, and location of the company. Here are ten common employee benefits that are often offered in the UK:
- Health insurance: Many companies offer private health insurance to their employees, which can provide access to healthcare services and treatments that are not covered by the National Health Service (NHS).
- Pension: Many companies offer a pension scheme to their employees, which is a way to save for retirement. Employers may contribute to the pension on behalf of their employees.
- Flexible working: Some companies offer flexible working arrangements, such as the ability to work remotely or to have flexible start and end times, to help employees balance their work and personal commitments.
- Annual leave: Most companies in the UK offer their employees a set number of days of paid annual leave each year.
- Maternity, paternity, and adoption leave: Companies are required by law to provide certain amounts of paid leave to employees who are expecting a child or adopting a child.
- Training and development: Many companies offer opportunities for employees to receive training and development to help them advance their careers.
- Employee assistance programs: Some companies offer support and resources to employees to help them manage stress and other personal issues.
- Employee discounts: Many companies offer their employees discounts on products or services that they produce or sell.
- Employee perks: Some companies offer additional perks to their employees, such as free or discounted gym memberships, company events, or company sports teams.
- Employee recognition: Some companies have programs in place to recognise and reward employees for their contributions and hard work. This may include things like employee of the month programs, awards, or other forms of recognition.
Should I offer my workforce employee benefits?
Yes, offering your employees benefits is a good way to attract and retain talent, improve employee satisfaction, and foster a positive work environment. Benefits can range from traditional offerings such as health insurance, retirement plans, and paid time off, to more innovative perks such as wellness programs, professional development opportunities, and flexible work arrangements.
Offering a comprehensive benefits package can also help your organisation stay competitive in the job market and demonstrate your commitment to your employees’ well-being. It can also help improve employee morale and motivation, which can have a positive impact on productivity and overall job performance.
However, it’s important to remember that the specific benefits you offer will depend on the size of your company, your budget, and your employees’ needs and preferences. It’s a good idea to regularly review and assess your benefits offerings to make sure they are meeting the needs of your workforce and helping you achieve your business goals.
Who is entitled to employee benefits?
Employee benefits are typically offered to full-time employees, although some employers may also offer benefits to part-time or temporary employees. The specific eligibility criteria for employee benefits can vary depending on the employer and the type of benefit in question.
For example, health insurance benefits may be offered to all full-time employees, while retirement benefits may only be available to employees who have completed a certain length of service with the company. Some employers also have waiting periods for new employees before they are eligible to enrol in certain benefits programs.
It’s important to carefully review the terms and conditions of any benefits program before enrolling and to consult with your HR department or an attorney if you have any questions or concerns. Additionally, it’s a good idea to regularly review and assess your benefits offerings to make sure they are meeting the needs of your workforce and helping you achieve your business goals.
Do I legally need to offer my employees benefits in the UK?
In the United Kingdom, there is no legal requirement for employers to offer employee benefits, although many employers choose to do so as a way to attract and retain talent and improve employee satisfaction.
However, there are some benefits that are required by law in certain circumstances. For example:
- Statutory Sick Pay (SSP): Employers are required to pay SSP to eligible employees who are unable to work due to illness for up to 28 weeks.
- Statutory Maternity Pay (SMP): Employers are required to pay SMP to eligible female employees who are absent from work due to pregnancy and childbirth for up to 39 weeks.
- Statutory Paternity Pay (SPP): Employers are required to pay SPP to eligible male employees who take time off work to care for a child during the first two weeks following the birth or adoption of the child.
- Auto-enrolment pensions: Employers are required to automatically enrol eligible employees in a workplace pension scheme and make contributions to the scheme on behalf of the employee.
These are just a few examples of the legal requirements for employee benefits in the UK. It’s important to consult with a qualified HR professional or an attorney to determine the specific requirements for your company and your jurisdiction.
Are there any downsides to offering my workforce benefits?
While offering employee benefits can have many benefits for both employees and employers, there are also some potential downsides to consider:
- Cost: Employee benefits can be expensive, especially if you offer a comprehensive package that includes health insurance, retirement benefits, and paid time off. The cost of these benefits can be a significant financial burden for small businesses.
- Complexity: Administering employee benefits can be complex, especially if you offer a variety of benefits that have different eligibility criteria and enrollment periods. This can increase the workload for HR departments and may require the services of a third-party administrator.
- Employee expectations: Once you start offering benefits, employees may come to expect certain benefits as part of their overall compensation package. If you are unable to maintain or improve your benefits offerings over time, it can negatively impact employee satisfaction and morale.
- Unintended consequences: Some employee benefits, such as paid time off, can have unintended consequences if employees take advantage of the benefits in a way that negatively affects the workplace. For example, excessive use of paid time off can reduce productivity and morale.
It’s important to carefully consider the potential downsides of offering employee benefits and to strike a balance that meets the needs of both employees and the business. This may involve offering a mix of traditional and innovative benefits, or considering alternative approaches to compensation and employee recognition.
What should I do if an employee insists their workplace benefits are not good enough?
If an employee expresses dissatisfaction with their workplace benefits, it’s important to take their concerns seriously and take steps to address the issue. Here are some steps you can take:
- Listen to the employee’s concerns: Start by listening to the employee’s concerns about the benefits package and understanding their specific needs and priorities. Ask questions and gather information to get a clear understanding of the situation.
- Evaluate the benefits package: Evaluate the current benefits package and consider whether it meets the needs of the majority of employees or whether it is time to make changes. Consider surveying employees to gather feedback and insights.
- Consider alternative benefits: Consider offering alternative benefits that may meet the needs of the employee, such as additional paid time off, flexible work arrangements, or professional development opportunities.
- Be transparent: Be transparent with the employee about the reasons why certain benefits are not available, and explain any budget constraints or legal limitations that may impact the benefits package.
- Keep the lines of communication open: Make sure the employee feels heard and valued, and keep the lines of communication open. Encourage the employee to share their thoughts and ideas, and keep them informed about any changes or updates to the benefits package.
It’s important to be proactive and responsive when employees raise concerns about their benefits, as this can help to build trust and improve employee satisfaction and engagement. Additionally, regularly reviewing and improving your benefits package can help to attract and retain talented employees, and support the long-term success of your business.
Are employees entitled to negotiate their benefits before they join a new organisation?
Whether employees are entitled to negotiate various benefits before joining a new organisation can depend on the specific policies and practices of the organisation, as well as the laws and regulations of the jurisdiction in which the organisation operates.
In many cases, employee benefits are determined by the employer and may not be subject to negotiation. However, some organisations may be willing to consider requests for changes to the benefits package, particularly if the employee has unique needs or circumstances that the standard benefits package does not accommodate.
It’s important for employees to understand the benefits offered by a potential employer before accepting a job offer, and to ask about any benefits that are important to them. If an employee is interested in negotiating a different benefits package, they should communicate their needs and concerns to the potential employer, and be prepared to discuss the reasons for their request and the impact it may have on the organisation.
Ultimately, the ability to negotiate employee benefits will vary from organisation to organisation, and it’s important for both employers and employees to understand the laws and regulations that apply to employee benefits in their jurisdiction. Employers and employees should also consider the impact of any changes to the benefits package on the overall cost and competitiveness of the organisation, and work together to find a mutually acceptable solution.
What are the best online resources for employers to find out more about employee benefits?
There are many online resources available to help employers learn more about employee benefits and find the best options for their business. Some of the best resources include:
- Government websites: The websites of government agencies, such as the U.S. Department of Labor and the U.K. Government’s GOV.UK, provide detailed information on employee benefits laws and regulations, as well as guidance and resources for employers.
- Industry associations: Industry associations, such as the Society for Human Resource Management (SHRM) in the U.S. and the Chartered Institute of Personnel and Development (CIPD) in the UK, offer information, best practices, and tools to help employers understand and manage their benefits.
- Employee benefits providers: Employee benefits providers, such as insurance companies, 401(k) providers, and flexible benefits platforms, offer a wealth of information and resources on the benefits they offer, including details on cost, coverage, and eligibility requirements.
- Online forums and communities: Online forums and communities, such as LinkedIn groups and online discussion boards, provide a platform for employers to connect with other benefits professionals, ask questions, and share best practices.
- Blogs and articles: There are many blogs and articles written by benefits experts and HR professionals that provide insights and advice on employee benefits, including information on the latest trends and innovations in the field.
By exploring these resources, employers can gain a deeper understanding of the employee benefits landscape and find the best options for their business and employees. Additionally, it’s always a good idea to consult with a qualified HR professional or an attorney to ensure compliance with applicable laws and regulations.








